Radon
On this page
- Radon: Background
- Health Risk of Radon
- Radon Levels
- Measuring Radon
- Reduce Radon Levels
- Follow-Up Testing
- Renovations After Lowering Radon Levels
- Funding
Radon: Background
Radon is a radioactive gas formed naturally by the breakdown of uranium in soil and rock. It is invisible, odourless and tasteless and it moves freely through the soil.
In enclosed spaces, radon can accumulate to higher levels and become a health hazard. Indoor radon concentrations fluctuate but are generally higher in the winter than in the summer and are generally higher at night than during the day due to sealing of buildings (closing windows, doors, etc.).
Video: National Collaborating Centre for Environmental Health: Radon
Video: Health Canada – Radon: What you Need to Know
Health Risk of Radon
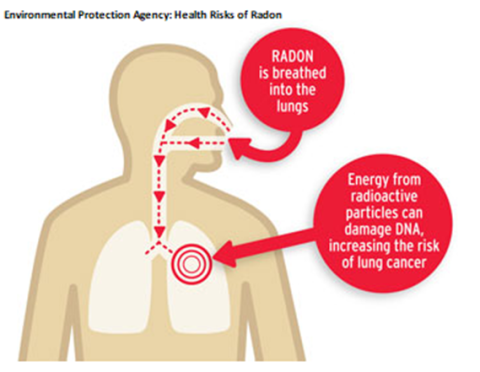
Radon gas breaks down to form radioactive elements which can be inhaled into the lungs and continue to breakdown and cause damage to the lung cells. When the lung cells are damaged, they have the potential to result in cancer when they reproduce.
Learn about what radon is, where it comes from, and how you can protect your health.
The health effects depend on the levels of radon and how long a person is exposed. Long term exposure to high levels of radon may increase the risk of developing lung cancer. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking and the leading cause of lung cancer for non-smokers. A lifelong smoker not exposed to radon has a 1-in-10 risk of developing lung cancer. When exposed to high levels of radon, that risk increases to 1-in-3. Non-smokers exposed to the same levels of radon have a 1-in-20 risk of developing lung cancer.
There is no evidence to suggest radon exposure causes other harmful health effects (other forms of cancer, respiratory diseases, etc.).
Radon in Drinking Water
There is no Canadian guideline for radon in drinking water. When radon is produced in the ground it can accumulate in water used for drinking. When that water becomes agitated (e.g. used for daily household requirements), the radon gas escapes from the water into the air. Research has shown that drinking water containing radon is far less harmful than breathing in the gas.
The health risk associated with radon comes from inhaling the gas, not from consuming radon.
Radon Levels
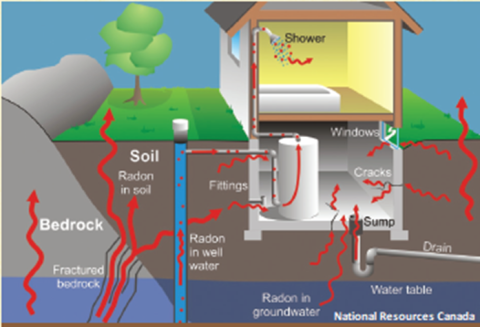
The pressure inside a building is generally lower than in the soil surrounding the foundation which allows air and other gasses, including radon, to be drawn inside from the soil.
Uranium is a common element found in the earth’s crust, so radon gas can be found in most buildings that contact the ground. Radon can enter a building through dirt floors, cracks in foundation walls and floors, sumps, cavities inside walls, gaps around pipes and basement drains. Radon can easily move through concrete block walls because they are porous.
Possible Radon Entry Points:
Learn about what radon is, where it comes from, and how you can protect your health.
Radon levels vary significantly across Canada, so it is impossible to predict whether a building will have a high level. The amount of radon in a building depends on the soil characteristics, construction type, foundation condition, occupant lifestyle and the weather.
Canadian Guideline
The Canadian guideline for maximum indoor radon level is 200 Bq/m3. Bq = Becquerel, a unit to describe one radioactive disintegration per second. The Canadian guideline is based on an exposure period of approximately 70 years spent in a dwelling that contains elevated levels of radon 75% of that time.
If you have tested, and the radon level is above the Canadian guideline of 200 Bq/m3, you should take action to lower the level. The higher the radon concentrations, the sooner action should be taken to reduce levels as practically possible.
If radon testing results are above the Canadian guideline, hire a certified radon professional to determine the best and most cost-effective way to reduce the radon level. The higher the radon level, the sooner you should mitigate. Health Canada recommends using a contractor certified as a radon mitigation professional. Contact any of the following agencies to find one:
• Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program – 1-855-722-6777 or info@c-nrpp.ca
• Canadian Association of Radon Scientists and Technologists – info@carst.ca
• Health Canada – radon@hc-sc.gc.ca
Measuring Radon
The only way to know if there are high levels of radon in an enclosed space is to test. Because radon levels can change over time, measurements taken over a longer period are more accurate.
Health Canada recommends completing a long-term radon test, for a minimum of three months, during the fall or winter. The detector should be placed in the lowest level of the building where occupants spend a minimum of 4 hours per day. A three-month test represents a person's annual average exposure and should be used to determine if the radon concentration exceeds the Canadian guideline.
Do-it-Yourself Kit
Do-it-yourself test kits can be ordered online through the Lung Association of Nova Scotia and PEI or Take Action on Radon. Kits can also be borrowed from the Provincial Library Service.
Closely follow the instructions on how to set up the test. To get an accurate measurement, a few kits should be placed in your home in various locations (in the basement and where you spend most of your time).
Hire a Professional Radon Measurement Service Provider
Certified radon measurement service providers can be found online through the Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program.
Make sure anyone hired is certified and will conduct a long-term test.
Reduce Radon Levels
Steps that can be taken to reduce radon levels indoors include increasing ventilation, sealing cracks and openings in foundation walls and floors, sealing cracks and openings around pipes and drains, and renovating existing basement floors, especially earth floors. The effectiveness of these strategies will be limited depending on the radon level and the unique characteristics of the building.
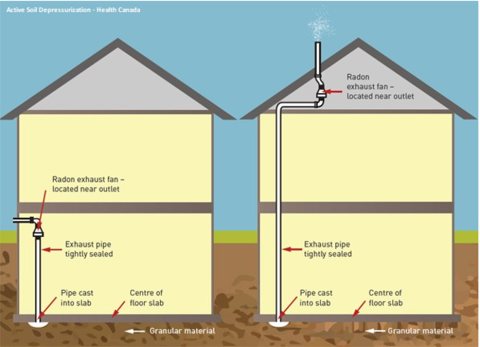
The most common method to reduce radon is by active soil depressurization, completed by a professional. A pipe is installed through the foundation floor and connected to the outside. A fan draws radon from under the building, before it gets inside, and releases it outside. The radon is diluted once it mixes with the outside air.
Active Soil Depressurization
Learn about what radon is, where it comes from, and how you can protect your health.
National Building Code
In 2010, new National Building Codes were introduced to protect against radon which included requirements for new homes to have a vapour barrier to reduce the entry of radon and a ‘rough-in’ for a radon reduction system which will significantly lower costs if future action to reduce radon is required. PEI adopted the National Building Code in 2020.
Follow-Up Testing
If a radon reduction system is installed, a certified professional should complete a short-term test at least 24 hours after a system is activated to demonstrate that it is working effectively. The test should ideally be in the same location where the measurements were originally made.
The building contact should complete a long-term three-month test the following fall/winter season to confirm that the annual average radon level has been reduced to below the Canadian guideline. To avoid conflict of interest, the test should not be performed by the company that installed the radon mitigation system.
Renovations After Lowering Radon Levels
If renovations are completed after a radon reduction system has been installed, ask the radon contractor what should be done to help ensure that radon levels continue to be reduced. After renovating, retest to make sure the construction did not reduce the effectiveness of the radon reduction system.
Funding
Financial funding for radon remediation is available through the Canadian Lung Association or the PEI Home Renovation Program.
More Information
Government of Canada – Radon
Canadian Guideline for Radon
Government of Canada – Radon: Reduction Guide for Canadians
Canadian Lung Association
Lung Association of Nova Scotia and PEI
Canadian Cancer Society
